Install/2-2/Networking: Difference between revisions
From Convention Master Documentation
Silvershock (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Silvershock (talk | contribs) (Updating Netplan syntax) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
The contents of the file will look something like this: | This file may also be called <code>00-installer-config.yaml</code>, or something else depending on how you set up your Ubuntu Server installation. The contents of the file will look something like this: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="yaml"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="yaml"> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
ethernets: | ethernets: | ||
enp0s3: | enp0s3: | ||
dhcp4: true | |||
version: 2 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
ethernets: | ethernets: | ||
enp0s3: | enp0s3: | ||
addresses: | addresses: | ||
- 10.10.1.99/24 | |||
dhcp4: false | dhcp4: false | ||
nameservers: | nameservers: | ||
addresses: [8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4] | addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4] | ||
# Default Gateway Config | |||
routes: | |||
- to: default | |||
via: 10.10.1.1 | |||
version: 2 | version: 2 | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:18, 15 December 2022
<< Previously: 2.1 - The Joe Editor
Configure Networking
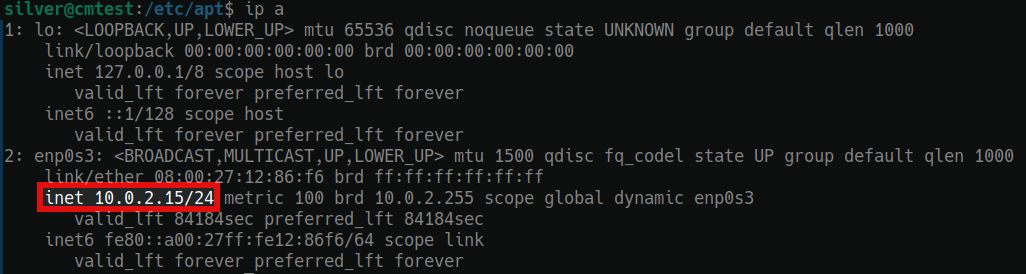
Find out your server's current IP address by logging in to your server and running the command:
ip a
Go to the Netplan configuration directory and open your network config file. Depending on how you installed Ubuntu, this could be 01-netcfg.yaml, 50-cloud-init.yaml, or something else.
cd /etc/netplan
sudo joe 50-cloud-init.yaml
This file may also be called 00-installer-config.yaml, or something else depending on how you set up your Ubuntu Server installation. The contents of the file will look something like this:
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: true
version: 2
This is a DHCP (automatic IP) setup on the network interface "enp0s3". Change it to look something like this (will vary depending on your network setup):
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
addresses:
- 10.10.1.99/24
dhcp4: false
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4]
# Default Gateway Config
routes:
- to: default
via: 10.10.1.1
version: 2
The above sample configuration would give your server the address 10.10.1.99. The gateway of your network can be anywhere but is generally at address "1" of the range. The DNS nameservers configured here are Google's. You may have different DNS servers to input instead.
Note: As this file is a YAML file, indentation is important. If you do not indent the lines so that they are in a correct hierarchy as above, you will receive an error when running the commands below.
Apply the networking changes
sudo netplan apply
You should now be able to access your server. You can run
ifconfig
to confirm the IP has changed.